
- EUR/USD fluctuates slightly above 1.1600 in the European session on Wednesday.
- Markets assess the Fed’s rate outlook following June inflation data.
- Technical sellers could take action in case 1.1600-1.1590 support fails.
After losing more than 0.5% and touching its lowest level in three weeks near 1.1590 on Tuesday, EUR/USD edges higher and trades above 1.1600 in the European morning on Wednesday. The pair’s near-term technical outlook suggests that the bearish bias remains intact following a correction from oversold levels.
The US Dollar (USD) gathered strength following the June inflation data and caused EUR/USD to turn south.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported on Tuesday that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 2.7% on a yearly basis in June. This reading followed the 2.4% increase recorded in May and came in line with the market expectation. Following this data, the probability of the Federal Reserve (Fed) lowering the policy rate by 25 basis points in September declined toward 50% from nearly 70% in the previous week, as per CME FedWatch Tool. In turn, the USD Index, which tracks the USD’s performance against a basket of six major currencies, gained about 0.6% on the day.
Later in the day, the US economic calendar will feature Producer price Index (PPI) data for June. A significant increase in the monthly figure could boost the USD with the immediate reaction and cause EUR/USD to continue to stretch lower.
Investors will also pay close attention to comments from Fed policymakers. If officials downplay the June inflation data, the USD could have a difficult time outperforming its rivals.
EUR/USD Technical Analysis
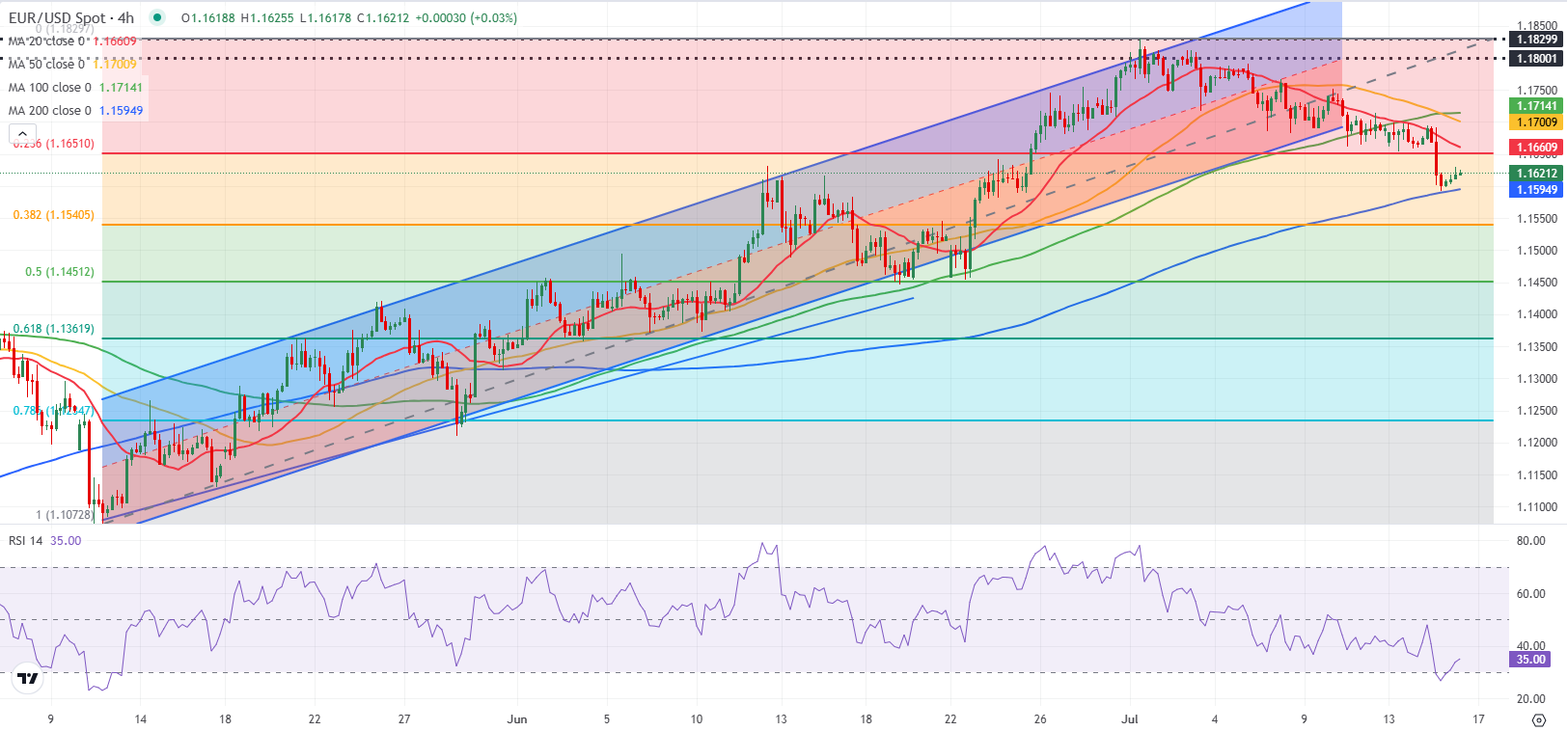
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator on the 4-hour chart stays below 40 after rebounding from below-30, suggesting that the latest recovery is a technical correction rather than the beginning of a reversal.
On the downside, 1.1600-1.1590 (static level, round level, 200-period Simple Moving Average) aligns as a strong support area before 1.1540 (Fibonacci 38.2% retracement level of the latest uptrend) and 1.1500 (static level, round level). Looking north, resistance levels could be spotted at 1.1660 (Fibonacci 23.6% retracement) and 1.1715 (100-period Simple Moving Average).
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
Information on these pages contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Markets and instruments profiled on this page are for informational purposes only and should not in any way come across as a recommendation to buy or sell in these assets. You should do your own thorough research before making any investment decisions. FXStreet does not in any way guarantee that this information is free from mistakes, errors, or material misstatements. It also does not guarantee that this information is of a timely nature. Investing in Open Markets involves a great deal of risk, including the loss of all or a portion of your investment, as well as emotional distress. All risks, losses and costs associated with investing, including total loss of principal, are your responsibility. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of FXStreet nor its advertisers. The author will not be held responsible for information that is found at the end of links posted on this page.
If not otherwise explicitly mentioned in the body of the article, at the time of writing, the author has no position in any stock mentioned in this article and no business relationship with any company mentioned. The author has not received compensation for writing this article, other than from FXStreet.
FXStreet and the author do not provide personalized recommendations. The author makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of this information. FXStreet and the author will not be liable for any errors, omissions or any losses, injuries or damages arising from this information and its display or use. Errors and omissions excepted.
The author and FXStreet are not registered investment advisors and nothing in this article is intended to be investment advice.





