- AUD/USD started the week on the back foot and broke below 0.6400.
- The US Dollar remained on the defensive following dovish Fedspeak.
- Australian flash PMIs surprised to the upside in June.
The Australian dollar tumbled sharply against the US Dollar (USD) at the beginning of the week, pushing AUD/USD south of the 0.6400 support for the first time since mid-May.
In addition, the pair broke below its critical 200-day simple moving average (SMA), near 0.6430, opening the door to the continuation of the ongoing bearish move.
Diverging monetary policies
The Reserve Bank of Australia’s (RBA) decision in early June to reduce its cash rate by 25 basis points to 3.85%, accompanied by guidance for a gradual decline to 3.20% by 2027, has put the Australian dollar under renewed pressure.
In contrast, the Federal Reserve opted to leave rates unchanged at its latest meeting, reiterating expectations for two half-percentage-point cuts by year-end yet acknowledging internal debate over the pace and timing of any easing.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell cautioned that US goods inflation could rise this summer as President Trump’s tariffs feed through to consumer prices, underscoring the Fed’s delicate balancing act amid ongoing trade tensions and geopolitical uncertainty.
China’s mixed signals
Australia’s fortunes remain closely tied to demand from its biggest trading partner.
Beijing’s May data showed an uptick in industrial production, retail sales and service-sector growth, supporting year-on-year expansion above 5%.
However, concerns linger over a slumping property market and the tapering of stimulus measures, casting doubt on momentum into late 2025.
Technical outlook
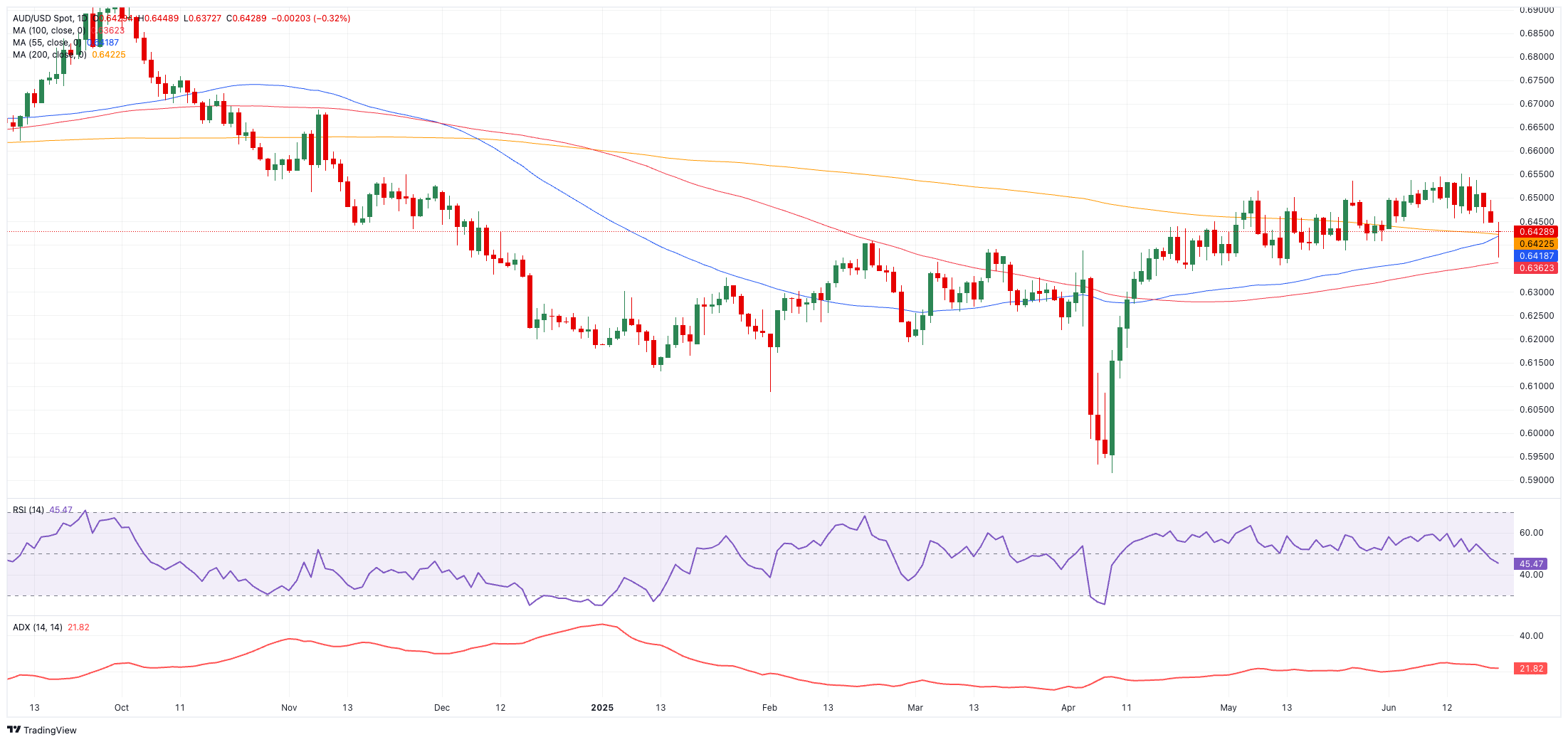
On the daily charts, immediate resistance sits at this year’s peak of 0.6551 (June 16). A decisive break above that could see the pair challenge November’s 2024 peak at 0.6687 and the 2024 ceiling at 0.6942.
To the downside, support looms at the June base of 0.6372, followed by May’s trough of 0.6356.
The momentum indicators are pointing lower: the Relative Strength Index (RSI) has dropped towards 45, indicating a potential further correction, and an Average Directional Index (ADX) hovering around 24 indicates a moderately strong trend.
AUD/USD daily chart
What’s ahead
Investors will turn their attention to the RBA’s Monthly CPI Indicator on June 25.
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for Australia. Decisions are made by a board of governors at 11 meetings a year and ad hoc emergency meetings as required. The RBA’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means an inflation rate of 2-3%, but also “..to contribute to the stability of the currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and welfare of the Australian people.” Its main tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will strengthen the Australian Dollar (AUD) and vice versa. Other RBA tools include quantitative easing and tightening.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for currencies since it lowers the value of money in general, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Moderately higher inflation now tends to lead central banks to put up their interest rates, which in turn has the effect of attracting more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in the case of Australia is the Aussie Dollar.
Macroeconomic data gauges the health of an economy and can have an impact on the value of its currency. Investors prefer to invest their capital in economies that are safe and growing rather than precarious and shrinking. Greater capital inflows increase the aggregate demand and value of the domestic currency. Classic indicators, such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can influence AUD. A strong economy may encourage the Reserve Bank of Australia to put up interest rates, also supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a tool used in extreme situations when lowering interest rates is not enough to restore the flow of credit in the economy. QE is the process by which the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) prints Australian Dollars (AUD) for the purpose of buying assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from financial institutions, thereby providing them with much-needed liquidity. QE usually results in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops buying more assets, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It would be positive (or bullish) for the Australian Dollar.
Information on these pages contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Markets and instruments profiled on this page are for informational purposes only and should not in any way come across as a recommendation to buy or sell in these assets. You should do your own thorough research before making any investment decisions. FXStreet does not in any way guarantee that this information is free from mistakes, errors, or material misstatements. It also does not guarantee that this information is of a timely nature. Investing in Open Markets involves a great deal of risk, including the loss of all or a portion of your investment, as well as emotional distress. All risks, losses and costs associated with investing, including total loss of principal, are your responsibility. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of FXStreet nor its advertisers. The author will not be held responsible for information that is found at the end of links posted on this page.
If not otherwise explicitly mentioned in the body of the article, at the time of writing, the author has no position in any stock mentioned in this article and no business relationship with any company mentioned. The author has not received compensation for writing this article, other than from FXStreet.
FXStreet and the author do not provide personalized recommendations. The author makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of this information. FXStreet and the author will not be liable for any errors, omissions or any losses, injuries or damages arising from this information and its display or use. Errors and omissions excepted.
The author and FXStreet are not registered investment advisors and nothing in this article is intended to be investment advice.








